In part 1 of this article, I explained the main supplements for muscle mass and strength, endurance, and recovery. The second part will discuss supplements for weight loss and general health. We will discuss such supplements as Ephedrine fat burners, L-carnitine, Multivitamins, Vitamin D, mega-3 fatty acids, Probiotics, and simply the benefits of the calorie reduction diet and exercise. Also, at the end of this article, I will give you a general overview of supplements with strong and poor evidence of effectiveness. Now, let’s start with the supplements for weight loss.
Weight loss supplements
Ephedrine/’fat burners’/thermogenic supplements
The main ingredient in different fat burners is ephedrine, which is a synthetic version of Chinese herb Ephedra or MA Huang. Ephedrine is more a drug than a supplement, which is a powerful central nervous system stimulant. The main effects of ephedrine are increased metabolic rate (up to 5%) and energy expenditure. Also, it can suppress your appetite and makes you more active. Athletes use it because it increases alertness, motivation, and performance. But on the other hand, it increases your heart rate and blood pressure. It is often combined with caffeine and aspirin to give a better effect, which increases the risk of side effects such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, palpitations, anxiety, nervousness, vomiting and dizziness. At very high doses, ephedrine can cause a heart attack and can even be fatal. Because of all the side effects of ephedrine, I would strongly recommend to avoid it. Plus, according to studies, the fat burning effect of ephedrine seems to decrease over time (weight loss slows or stops after 12 weeks).
Ephedrine-free fat burners
Some weight loss supplements claim to give similar effects to ephedrine but without harmful side effects. The main ingredients in these products include green tea extract, bitter orange extract and others. While the herbal alternatives to ephedrine are generally safer, you still can get side effects with high doses. All these ephedrine-free fat burners can increase your blood pressure and cause different heart disturbances. Also, according to research, the impact of these fat burners is relatively small or has no effect at all. The only positive data is for green tea, but you would need to drink at least six cups daily to achieve a significant fat-burning effect. Overall, a careful calorie intake and exercise would give you the best result in weight loss compared to any other supplement.
L-carnitine
Carnitine is a non-essential amino acid made by the liver from such amino acids as lysine and methionine. It is essential for energy production and fat metabolism. It can be found in such foods as meat and dairy. There are several types of carnitine, but most supplements sell acetyl-L-carnitine because it absorbs better. The main role of carnitine is to transport fatty acids into the mitochondria, where these fatty acids are burned to create usable energy.
Since L-carnitine helps you to move more fatty acids into your cells to be burned for energy, it should help you lose fat. Unfortunately, all studies showed negative results in terms of weight loss. Moreover, some of the participants in these studies experienced nausea or diarrhea. There are no severe side effects while taking L-carnitine supplements. However, there are no positive results either.
Calorie reduction diet and exercise.
All in all, as you can see, no magical pill can help you get rid of excessive weight. An adequately organized diet and exercise is the best way to reduce body fat. To get more information on creating a weight loss diet, read my article: “Your step-by-step weight loss program”. About the best exercises for weight loss, read my article: “What is the best exercises for weight loss”.
Supplements for general health
Multivitamins
Multivitamin and mineral supplements are available in pills, powders, and liquid forms. Many people, especially athletes, think that it is mandatory to take them to support their training. But is it necessary, or is it just a wasting of money. Of course, athletes have higher energy needs than average people and need more vitamins and minerals in their diet. However, they must understand that vitamins and minerals taken in high doses from supplements can be harmful (especially fat-soluble vitamins). As to real food, it’s almost impossible to overdose on vitamins and minerals from real food.
The best advice in this situation would be to consult a doctor or dietitian before taking supplements. After the doctor analyzes your diet, he will give you appropriate advice about whether supplement is necessary or not. And even then, if you lack some micronutrients, you should first try to get all the nutrients from your diet. When getting all the nutrients from a well-balanced diet is impossible, supplements can be taken. Athletes who will probably need extra supplementation would be those with high sweat and urine losses (losing electrolytes and zinc), athletes with low energy intake or specific dietary preferences (vegetarians and vegans). Vitamin D concentrations may be low in athletes training and competing in winter sports or indoors. Iron stores can be compromised in athletes undertaking high intensity and endurance-based exercises.
Also, it is essential to understand that there are no additional benefits of taking extra micronutrient supplements to improve sports performance if you get enough nutrients from your diet. Beneficial effects can be observed only in athletes who start with low levels of vitamins and minerals in their bodies. In other words, taking supplements simply restores athletes’ stores to normal levels. If you are getting enough nutrients with food, there is no need for extra supplementation. Bellow, I will also put a table of all necessary vitamins and minerals that are especially important for an athlete.
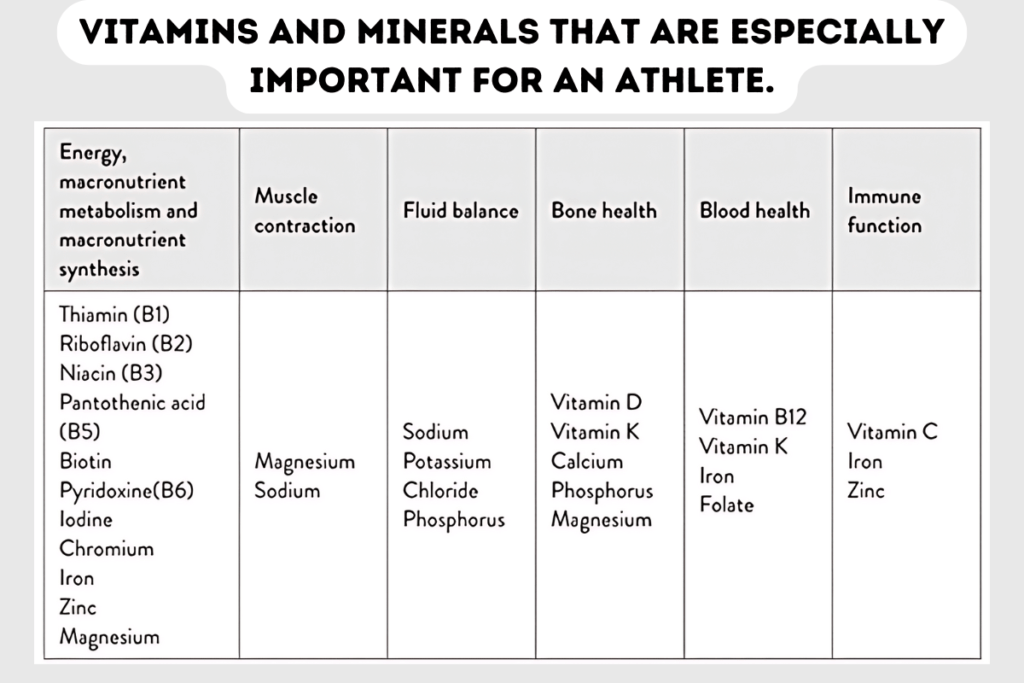
You can read more about all these necessary vitamins and minerals in my article “Why micronutrients from fruits and vegetables are so essential for sports performance.”
Vitamin D
We already spoke about multivitamins and whether you need them. Although vitamin D is the most important from them, and we should discuss it separately. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin which comes mainly from exposure to ultraviolet radiation (sun). It also can be obtained from foods like oily fish, egg yolk and fortified foods. We need vitamin D for optimal bone mass, muscular performance, and immune function. In other words, low levels of vitamin D may reduce muscle function and strength and can increase risk of injury and illness.
Several studies revealed that the athletic performance of athletes peaks in the summer months and declines in the winter months. The decline in athletic performance during winter happens for an obvious reason – not getting enough vitamin D from the sun. After such athletes were given vitamin D supplements for eight weeks, their performance significantly improved. In other words, correcting vitamin D deficiency using supplements helped to improve athletic performance. So, from April to September, it is essential to get enough vitamin D from the sun (the best way to get vitamin D). No supplements are needed during these months. But, from October till March it would be wise to take extra vitamin D supplements for sport performance and better immune health.
The safe upper limit of vitamin D is 25 micrograms. Toxicity is rare but may occur in doses over 250 micrograms. Symptoms of toxicity are weakness, muscle pain, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and thirst. Also, it is important to understand that, like with other supplements, vitamin D will work if you are deficient in vitamin D. Before taking the supplement, consult with your doctor, who may recommend a simple blood test to find out if you are deficient in vitamin D.
Fish oil/omega3 fatty acids
Fish oil contains two unsaturated fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). We can get these unsaturated fatty acids primarily from oily fish like tuna, cod (liver) and salmon. Also, our body can convert alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) into omega-3 fatty acid, although with poor efficiency. We can get ALA fatty acid from rapeseed oil, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds. Omega-3 fatty acids are involved in many processes in our body, including reduction of heart disease risk, cancer, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity and increase in HDL (good cholesterol). Also, for athletes omega-3 supplements can help reduce inflammation, including post exercise muscle soreness, improve muscle functioning, blood vessel elasticity and delivery of oxygen to muscles.
To get the necessary amount of omega-3, it is enough to eat 2 two portions of oily fish per week, but if you are not eating oily fish regularly, then you can take two capsules of fish oil a day, which will provide you with approximately 600 mg of EPA and DHA. Sport people can easily increase this amount till 1000 mg a day. Very high doses (more than 3g/day) may increase the risk of internal bleeding. So, don’t overdose and ideally, try to get all necessary omega-3 fatty acids from oily fish.
Probiotics
Probiotics are the live microorganisms (bacteria) that live in our gut and are crucial for optimal intestinal health, digestion, and immune function. They can be found in different yoghurts and other cultured milk products. Also, you can buy them as capsules, powders, or tablets. Probiotic supplements help us by crowding out disease-causing bacteria and increasing the number of good bacteria. This helps to strengthen and restore the balance of intestinal flora. Probiotics can also help to improve the bioavailability of nutrients. No significant side effects have been reported. You can use probiotics with pills or ingest them from yoghurts, which would be a cheaper alternative.
Conclusion
Now, let’s sum up everything we said above and decide on supplements you can use for muscle strength, endurance, recovery, weight loss, and general health. First, I do not want to sound annoying, but it is necessary to repeat that there is no replacement for a well-balanced diet that can provide you with all the essential macro and micronutrients. Before buying supplements, think about how you can get the same benefits from a balanced diet. You must remember that supplements have a risk of contamination with prohibited substances not listed on the label.
Next, all sport supplements we can divide into several categories: ergogenic aids (are used to improve athletic or physical performance), nutritional supplements (to supplement the nutrient intake of the diet), supplements for weight loss and general health. The best supplements for general health would be omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and multivitamin supplements. However, if you eat a balanced diet, you should get all these nutrients from your diet alone. There is no need to spend money on supplements when you can get all the nutrient from food alone. Eating a calorie-reducing diet and exercising is the best way to lose weight.
As to dietary supplements, they could be beneficial for athletes who are larger in size or engaged in high volume/intense training (such athletes may need 5000 or even 10000 kcal/day); Next would be athletes with a busy training and competitive schedule, also those who travel a lot; And lastly, those athletes who engage in sports that benefit from rehydration or refueling during an event and when a sit-down meal is impractical. Basically, when you need a meal on the go, that will digest and absorb quickly and give you immediate extra energy.
There are plenty of ergogenic supplements, and you should probably try them all and see what is working the best for you. You always need to look on your personal goals first, then on your budget, what supplements you can allow to yourself and what is better to get from the diet. If you would have a limited amount of money and could buy just one supplement, its better to buy creatine (the best first supplement for beginners). If you have extra money to buy one more supplement, then go for protein, and I would choose casein protein to take it before bedtime to save your muscles from breakdown during sleep. As to endurance and recovery, I would say the best pre-workout is simple carbs that you can get from food alone. On top of that, you could try caffeine, beta-alanine, bicarbonate and beetroot juice. This is what really can help you to improve your endurance at the gym. But again, look at your goals first, how much money you can spend on supplements, and always think that some of these things you can get from food alone, which would be better and much cheaper. All in all, below, I also show a table of supplements that are worth trying and which are better to avoid because they don’t work or are even dangerous and can give you unnecessary side effects.
Supplements for muscle mass, strength, endurance and recovery.
| Endurance and recovery | Muscle mass and strength | |
| Strong evidence | Carbohydrates (drinks, bars, and gels) Caffeine Beetroot juice and other nitric oxide supplements Beta-alanine Bicarbonate | Creatine Protein |
| Moderate evidence (or easily can be obtained from A diet alone) | Antioxidants Glutamine Taurine | BCAA HMB ZMA |
| Pour of evidence or prohibited | Pre-hormones/pro-hormones Steroid precursors/testosterone boosters |
Supplements for weight loss and general health.
| Weight loss | General health | |
| Strong evidence | Calorie-reduced diet and exercises | Probiotics Vitamin D |
| Moderate evidence (or easily can be obtained from A diet alone) | Caffeine, green tea | Multivitamins Omega 3 fatty acids |
| Lack of evidence or prohibited | Ephedrine/fat burners Ephedrine-free fat burners Other thermogenic supplements L-carnitine | Other |




