Carrying excessive body fat is a disadvantage in almost any sport. It can badly affect strength, speed, and endurance. In sports like running, cycling, sprinting, and combat sports, excessive body fat is always a problem. The only sport where fat could give a necessary advantage is sumo wrestling. Surplus fat is like unnecessary baggage that you must carry, and because of that, almost any sport requires the leanest body to win. So, the goal for the majority of athletes is to reduce body fat while maintaining lean mass to improve performance. But here is the question: “How do you achieve the leanest body while still staying healthy?” In this article, I will explain what percentage of body fat will give you the best performance and the dangers of body fat levels that are too low. Also, I will guide you on different methods to measure your body fat.
Simple methods to measure body fat.
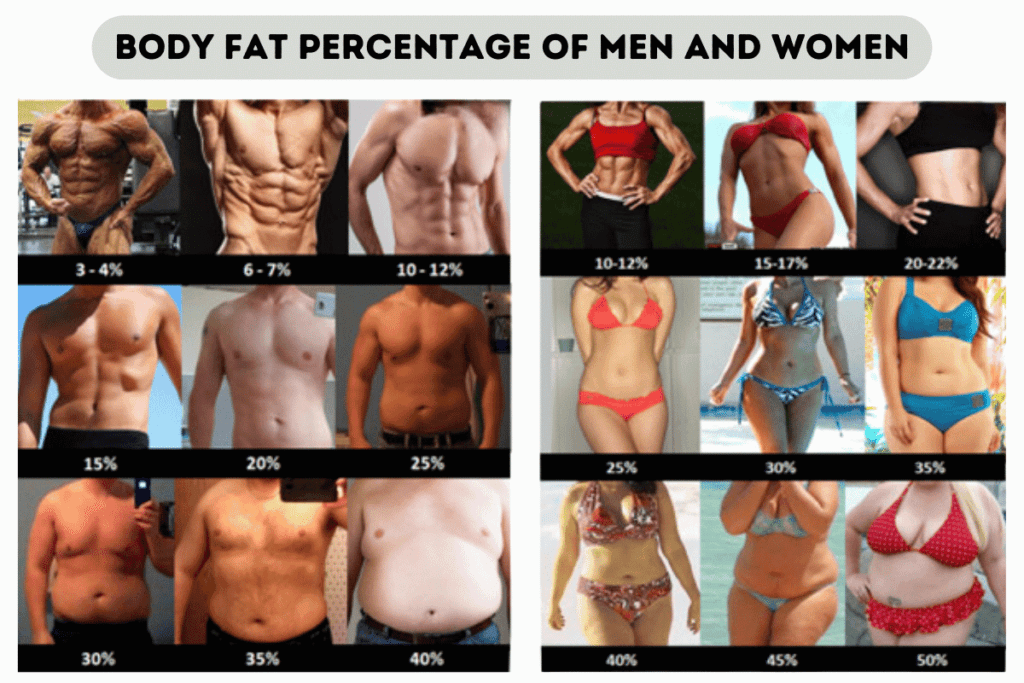
The easiest and quickest way to see how fat you are is to look in the mirror. You can easily find images of different levels of body fat just by typing in the Google search bar: “Body fat percentage.” You can find approximately your body fat percentage by comparing yourself to these images. It’s not the best and most accurate way to find out your body fat, but it is the easiest one. One of the pictures below shows an example.
The following method to determine how fat you are is to use scales and measuring type. This method will not give you exact measurements of your body fat, but it will show you if your diet for weight loss is working or not, and it will show you what exactly you are losing during weight loss: fat or muscles. It is essential to use measuring type together with scales. Using just scales is not recommended because of several reasons. Scales can show you just your overall weight. But because your weight consists of fat-free mass (FFM) and fat mass, it is difficult to say precisely what you are losing: fat or muscle. Fat-free mass includes muscles, organs, bones, and blood. Fat mass consists of fat stored as an energy source, fat in the central nervous system, bone marrow, and the fat surrounding your organs (essential fat). So, when standing on scales, you don’t know how much of that is fat mass and how much is a fat-free mass.
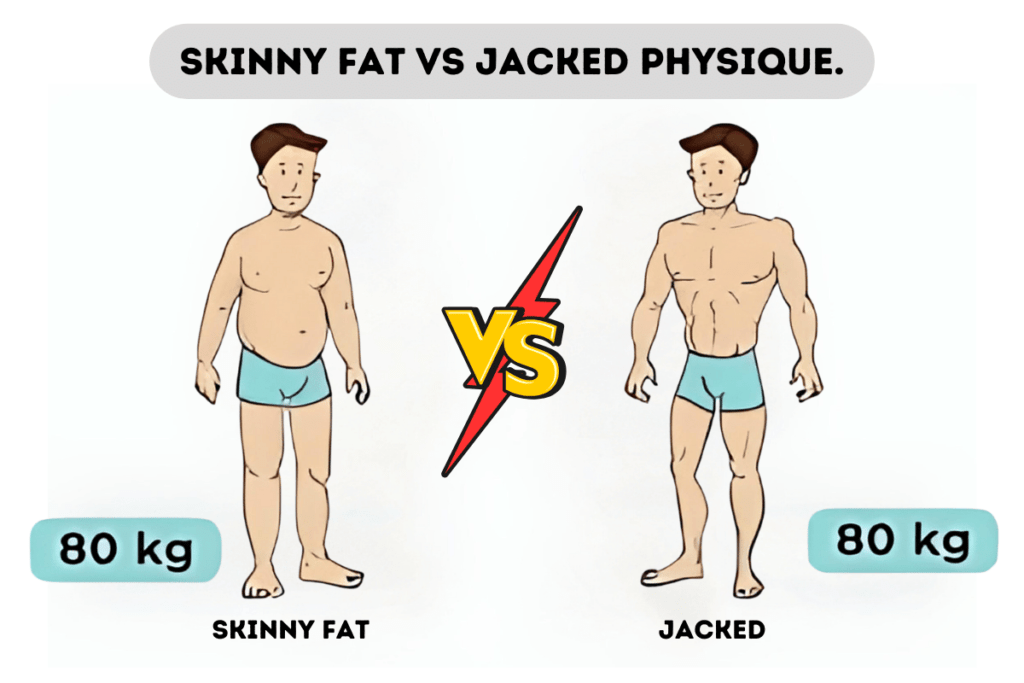
Also, if you are doing resistance training your weight can increase (scales will show that you have a bigger weight) because your muscles are growing, not fat. Or for example, when you are trying to lose weight and you go on a very restrictive diet, you can notice that your body becomes smaller, your scales show you that you lost weight, but your body still doesn’t satisfy you because now you look skinny and fat. This can happen because you lost weight by losing muscles, but amount of fat still stays the same. An example of such a situation can be seen below. So, relying only on scales is not a good idea.
Using the measuring tape, you must measure your chest, waist, hips, arms, and legs. The main result you want to see here is a decrease in waist circumference and an increase in muscles (or at least muscle size should stay the same). Muscles consist of fat as well, so a slight decrease in muscles during fat loss can be acceptable but should be as little as possible.
Also, you can add skinfold callipers to all these simple fat-measuring methods. This measurement method is widely available in many gyms, health clubs, and clinics. You can use it at home too. This calliper measures in millimetres the layer of fat just under the skin at various places on the body. Measurements are done on 3 to 7 specific areas (triceps, biceps, hip bone area, lower back, abdomen, thigh, and below the shoulder blade). After, you must use one of the equations, such as Jackson & Pollock, Parrillo, and Navy Tape, to calculate your body fat percentage.
Advanced methods to measure body fat.
One of the advanced methods of measuring body fat percentage is Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA). Such scales that give body fat percentage readings are now widely available in many gyms, sports clinics and health centres. They send a small electrical current through the body and measure its impedance or resistance. The body’s lean tissue is a good conductor of electricity (contains high levels of water and electrolytes), while fat is a poor conductor. Increased levels of fat mass result in a higher impedance value and correspond to higher levels of body fat. This means the more significant a client’s fat mass, the higher their impendence value. There are different types of such devices. The most accurate ones are those where a small electrical current is sent through your hands and feet (they are more expensive ones). To get a proper result of your body fat, you must be well hydrated when having a BIA measurement. If you are dehydrated, the current will not be conducted through your lean mass so well, giving you a higher body fat percentage reading.
Another advanced method of measuring body fat is hydrostatic weighing. Although hydrostatic weighing is the most accurate method, it is the least practical regarding expense, time, and equipment. It involves seating a person in a chair attached to scales and immersing them in a tank of water. This helps to calculate their body density from the relationship between their normal body weight and their underwater weight. Since bone and muscle are more dense than water, a person with a high lean mass will weigh more in water, indicating a lower fat percentage. And because fat is less dense than water, a person with a high-fat percentage will weigh less in water than on land.
Other good health indicators.
One of the methods to get a general picture of your health is to calculate your body mass index (BMR). Body mass index (BMI) helps to estimate whether your weight is within healthy limits. BMI is estimated by dividing your weight (in kg) by the square of your height (in meters). For example, if your body weight is 60 kg and your height is 1.7 meters, your BMI = 60/(1.7*1.7) = 21. Once you have calculated your BMI, you can use the table shown below to interpret it. For example, if your BMI is 25 – 29.9, then you are in the overweight or pre-obese category. If your BMI is 21, you are in a normal/average category.
| BMI | Classification |
| <18,5 | Underweight |
| 18,5 – 24,9 | Normal/average |
| 25 – 29,9 | Overweight/Pre-obese |
| >29,9 | Obese |
Doctors and health professionals use BMI to assess a person’s risk of getting certain health-related conditions, such as heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and so on. If your BMI is between 25 and 29,9, you are at increased risk. Those with a BMI above 30 are at a greater risk. And by the way, a BMI under 18,5 puts you at risk of other health problems as well. If your BMI is under 18.5, you are at risk of getting such health problems like respiratory disease, certain cancers and metabolic complications.
One of the drawbacks of BMI is that it does not give information about your body composition. It doesn’t show how much weight is fat and how much is muscle. It simply indicates a health risk for ordinary people, not sports people. For example, suppose you are a rugby player or bodybuilder. In that case, you can have a higher percentage of lean mass and a low percentage of body fat, and your BMI might misleadingly indicate that you are overweight or obese. But in reality, you have more muscle than average people. The same, body fat can be underestimated in individuals who has little muscle or who are very overweight. Also, BMI doesn’t consider where fat is stored in your body.
According to where your body fat is distributed, you will have a higher or lower risk of getting health problems. For example, fat stored primarily around the abdomen (visceral fat), carries a much more significant health risk than fat stored primarily around hips and thighs. This means that a person with high BMI and fat mainly around the hips will have less health risk than another person with the same BMI and fat distributed around abdomen. You can assess your body fat distribution using waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio methods.
According to scientists, waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio methods are more accurate than BMI in predicting type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure and so on, and they are quite easy to do. Table of waist measurements bellow shows waist measurements that indicate health risk levels. A waist circumference of 94 or more in men or 80 or more in women indicates excess abdominal fat. As to waist to hip ratio, to see how healthy you are, you need to divide your waist measurements by your height. It should be no more than half your height.
| Increased risk | Severe risk | |
| Men | Over 94 cm (37”) | Over 102 cm (40”) |
| South Asian men | Over 90 cm (35,5”) | |
| Women | Over 80 cm (32”) | Over 88 cm (35”) |
| South Asian women | Over 80 cm (32”) |
How accurate are all these methods and what method to choose.
First of all, choose the method that best fits your goals. If you are a professional bodybuilder, you will need more precise and accurate methods like underwater weighing, skinfold measurements (callipers) or bioelectrical impedance. If your goal is to be in good shape and stay healthy, then simple methods like measuring type and scales, BMI and waist measurements will be enough. So, in conclusion, the most accurate methods would be underwater weighting, skinfold measurements and bioelectrical impedance. Less accurate methods to measure body fat: mirror, scales and measuring type. Other good health indicators are BMI, waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio methods.